Colonialism has consistently been a force in the global purview, including the technological space. In recent years, the expansion of artificial intelligence has vastly increased corporations’ global influence. As the world’s technologies continue to advance and innovate, individuals must keep a watchful eye on the ways in which digital colonialism might repeat harmful practices from the past.
Envisioning the Future of Museum Accessibility Through Artificial Intelligence
With AI’s ability to automatically produce content and process complicated datasets with high accuracy, museums worldwide are exploring ways in which this innovative technology can help them better achieve their missions and advance accessibility efforts. Through case studies, learn about three applications of this technology: content digitalization, language accessibility, and visual description.
Part Two: Evaluating Neurodiverse Accessibility Offerings and Education Support in Art Museums
Art Museums are still falling short of accessibility needs. To better understand how art museums are addressing neurodiverse audiences, an evaluation was conducted of 30 Art Museums in three areas: neurodiverse accessibility offerings, physical accessibility offerings, and educator support and resources.
Part One: Understanding Neurodiverse Accessibility in Art Museums
For art museums, knowledge of and consideration of neurodiversity must be a requirement within the context of accessibility and DEAI efforts. How effectively are art museums actually providing neurodiverse accessibility, if at all? Additionally, what strategies can be implemented to enhance inclusivity for neurodiverse visitors and support educators who aim to bring neurodiverse students into these spaces?
Announcing 2024-2025 Research Themes and Outcomes
Whether artificial intelligence, blockchain, extended reality, or other developments, technology is hitting the creative sector from all angles. Regardless of where you sit within your organization, you are likely facing questions on how this emerging technology will impact your work. This year, we will continue to share content that sparks conversation and makes you rethink what is possible.
Digital Inequity's Impact On Arts Participation Pt. II
This is the second installment of research relating to digital equity and arts communities. The research discusses the potential role of media and digital arts in the fight toward digital equity, compares barriers to digital participation with arts participation, and explores the role of libraries as critical players in combatting digital inequity.
Digital Inequity's Impact on Arts Participation Pt. I
how does digital inequity impact the arts sector and how might the arts sector respond to the digital inequities in their communities? This research was compiled under the belief that the arts can have a role in combatting issues of equity and inclusion outside the field of arts and culture. The arts’ role in the broader public sphere can improve the lives of all members of a community. The hope for this research is to begin to understand how that can begin to take shape to address digital inequity.
Museum Audience Engagement with GIS
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) applications can connect museums with their communities in ways that make project management and decision-making informed and strategic. There are numerous ways that GIS maps can be used—they can provide a picture of who is visiting the museum and how they are interacting with the space once they are there. Additionally, they can aid visitors with their experience of museum collections.
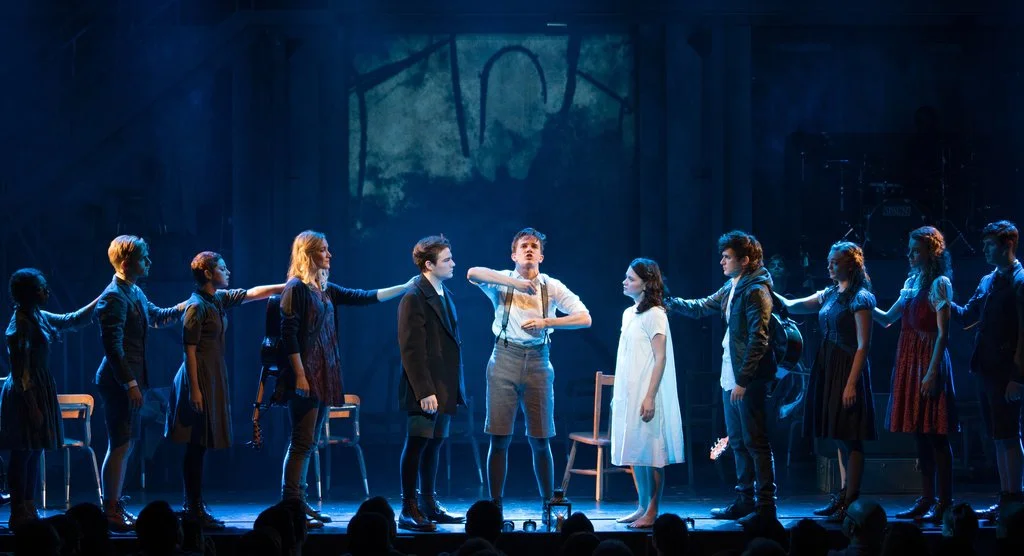
Equity Via Art and Technology: A Case Study of Deaf West’s “Spring Awakening”
This case study examines Deaf West Theater. Through weaving “American Sign Language (ASL) with spoken English to create a seamless ballet of movement and voice.”, Deaf West teaches through practice that (1) Language and linguistic identity can indeed advance and strengthen storytelling and (2) Audiences want to see linguistically diverse and accessible stories.
Enhancing Museum Accessibility with GIS
The Connection of Digital Placemaking and Inequity
Through a narrative-focused approach to digital placemaking, users gain an understanding of the environment they inhabit and perhaps a sense of “home.” However, A true collective experience cannot take place when certain populations lack the access and/or ability to participate in events, particularly in a digital space. Digital inequity has been entrenched as a significant barrier to education, employment, healthcare, and commerce in the 21st century.
The Current State of Linguistic Representation and Accessibility in the Artistic Sector
Language-based diversity and the related questions of physical accessibility are regularly left out of these conversations; whether conscious or not, DEI efforts in popular arts and media regularly function on the outskirts of language-based representation and accessibility. For members of minority and underrepresented demographic groups, representation in arts and entertainment not only impacts how the world sees them, but guides how they see themselves.
TBT: Education, Gamification, & Public Policy
Museums' Use of Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing is used by a variety of institutions, including the fine arts. For a review on its origins and use, read this article. Many museums are employing professional translation services. For instance, the Field Museum in Chicago uses a company called Multilingual Connections, and the Denver Botanical Gardens, South Florida Science Center, and the Metropolitan Museum of Art use a company called Eriksen Translation. That is, museums must pay for professional human translators in order to offer material in multiple languages. Besides machine translation’s promise of museums’ ability to better serve communities in America, the international museum industry also thrives off the ability to offer people a window into culture and identity that isn’t possible without accurate translations. The significant reduction of costs that would occur if machine translation improved would offer museums the ability to broaden their offerings and expand their visitor experience beyond their current capabilities.
Understanding Natural Language Processing
In a world where Siri can set alarms, give us directions, and look things up, shouldn’t machine translation be better by now? How does machine translation work? Why are museums still using human translation? And most importantly, what happens when machine translation is good enough that museums and other arts enterprises can use it without human oversight? Regardless of its shortcomings, Natural Language Processing has made profound developments within the past 5 or 6 years. While there is still much to be improved on, its integration into everyday life personally and professionally shows that this technology will only experience improvement in the future.
TBT: Innovation, Technology, & Theatre
Haptic Feedback: Feeling the Dance You Cannot See
Dance relies on the audience’s sense of sight to experience a performance. However, dancing itself is a very tactile experience. A dancer’s precise movements depend on a heightened internal awareness of the body – how joints are stacked and what muscles are activated. They must also maintain an awareness of external forces – how one limb moves in relation to the other, how their skin feels sliding against the floor, and where they sense other dancers moving with them in space.
The experience of the audience is vastly different from that of the dancer. Is there a way to bridge this divide and communicate a multi-sensory experience to the audience, and allow those who cannot see to feel? Tapping into this sense of touch might help audiences experience dance in a new way.
Open Access Initiatives & Its Impact on the Art World
According to the Western Museum Association, Open Access refers to efforts made by museums to provide high-resolution downloadable images free of charge to maximize the ability of the user to interact with, share, and reuse the images. In 2018, Douglas McCarthy, Collections Engagement Manager at Europeana, and Dr. Andrea Wallace, Senior Lecturer in Law at the University of Exeter, set out to see how many cultural heritage institutions make their digital collections available for free use, as well as how they do it. The pair created a Google Sheet survey that has listed over 1,200 international institutions, including Galleries, Libraries, Archives, and Museums. Over one-third of these records name specific Museums. While Open Access encompasses numerous industries, this article focuses Open Access technology and usage in the context of Museums and Artists.
Open Access and Why it Matters in the Museum Space
Amidst Covid-19, many museums moved to sharing collections and exhibitions virtually. However, even before Covid, museums began sharing their collections in a virtual, accessible manner with Open Access. It is estimated that nearly 1,000 cultural heritage institutions world-wide have published some or all of their collections with Open Access usage. While Open Access exists in other industries, such as in libraries, this article focuses on the context of Open Access in the museum space.
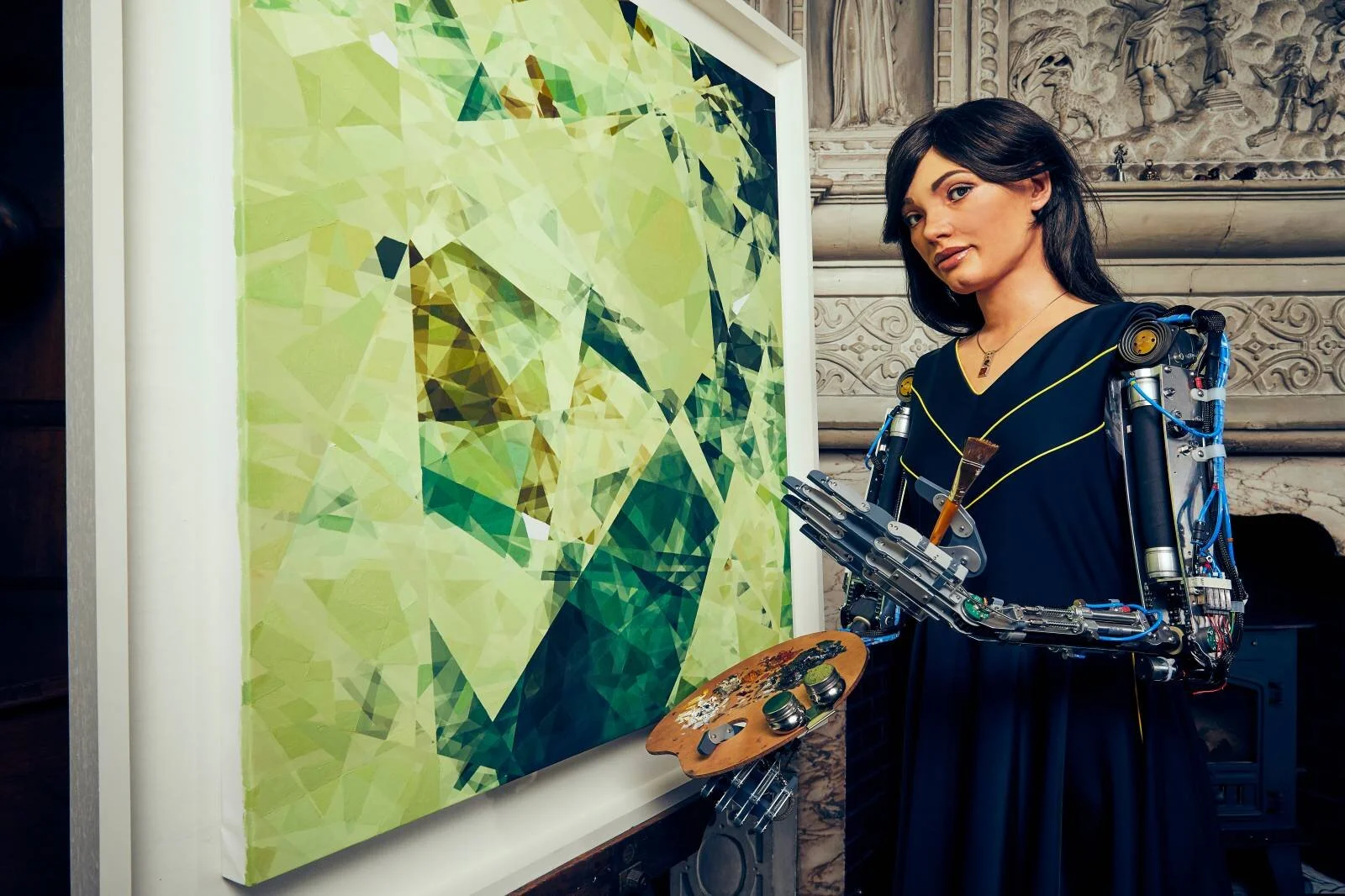
Could It Be Sentience or Just Expert Coding? The Emerging Role of Robots in the Arts
Few innovations represent the intersection of humanity and technology more famously than that of the robot. Like art, robots are the result of humanity’s urge to create something new in its own image – and, also like art, they have become an inescapable part of our world. In a post-pandemic world whose inhabitants have become accustomed to virtual experiences, these robotic arts roles, including facilitating virtual museum visits, performing through a computer program rather than a script, and creating what maybe approaching original and creative art, are probably here to stay.