By: Reese Lamping, Kai Ling Liu, Jai Ta, Hongyun Yu, Ziqi Zhou
The following article shares data and key findings on Live Service Game audiences as part of a research study conducted as a capstone team in the Master of Entertainment Industry Management at Carnegie Mellon University.
After seeing tremendous financial success, the market for live service games (LSGs) has become saturated, and with this increased competition, consumer expectations continue to shift and grow. In Part I: Best Practices in Live Service Game Campaigns, Heinz College Master of Entertainment Industry Management students dive into the background and success of these games. In Part II, the team has employed data-gathering methods such as interviews, a survey, and social listening to better understand factors influencing player engagement and retention. Read more about their methodology and findings below.
To provide a better understanding of the factors influencing player engagement and retention, the research team employed data-gathering methods such as interviews, a survey, and social listening. The team interviewed nine industry leaders to gain insights on effective campaign strategies and LSG pitfalls and risks. Additionally, an anonymous survey with 525 respondents focused on player preferences and experiences with LSG campaigns. The survey was distributed among gaming communities such as Discord servers, Reddit forums, and social media platforms. Secondary research including case studies, press releases, and public patch notes provided more thorough trend analysis and specific game analytics.
The team acknowledges that there was limited access to comprehensive player pools and proprietary data from gaming companies. Additionally, survey distribution was limited to the team’s personal network and accessible platforms.
Survey and findings
An online survey was conducted on gamer insights and sentiment on LSGs. The survey was open for approximately five weeks, starting on January 26, 2024 and closing on February 28, 2024. The survey was constructed using Qualtrics and distributed through various social platforms such as Discord, Twitter, Twitch, Reddit, LinkedIn, Instagram, and WeChat. Targeted survey participants were active gamers, defined as people who play video games at least three hours per week. People who identify themselves as no/little affiliation and play less than three hours per week were filtered out for not being statistically relevant to our study.
Participant Demographics
Our survey received a total of 525 responses. After filtering out non-gamers, there were 431 responses in total with 355 respondents having completed all demographic questions at the end of the survey. The respondents were 233 men (63%), 105 women (30%), 14 non-binary people (4%), and remaining participants who identified as other (3%). The majority of the respondents were aged between 20-29, accounting for 69% of the total participants. This might be due to the distribution of the survey amongst friends and peers of the team’s age group and the use of social platforms that skew towards a younger demographic. The top three race/ethnicity groups for our respondents were Caucasian (50%), Asian (37%), and Hispanic/Latino (9%).
Average Time Spent
According to the survey results, 22% of respondents spend 4-9 hours gaming weekly, 27% spend 10-19 hours, 24% spend 20-29 hours, and the remaining 27% spend more than 29 hours weekly. Additionally, 70% of respondents reported playing video games with their friends at least once per week. These results indicate that gaming is widely regarded as a social activity for many people. Moreover, when we asked respondents about their main reason for quitting a game and coming back, the most common responses were because of social reasons: “I stopped playing because I was no longer able to play with my friends […] started playing again when I found someone else that I could play with.”
Player Spending Behaviors
Based on these survey results, people are not spending a lot of money in-game on microtransactions for DLC, accessories, cosmetic skins, and battle passes. The mode for monthly spending is $0.00, the median is $10.00, while the average (excluding outliers) is $32.74. These numbers suggest that monetization fatigue is prevalent in cons’ frustration in the LSG space. A digital marketing executive interviewed for this study reinforced this finding:
It’s the top 10% who are spending the most amount of money. But there’ll be a huge chunk of players who are free to play and refuse to spend any money in gaming, and then there are those who don’t necessarily play loads of games, but will spend as much money as they need in order to get the furthest into the game[s they focus on] (digital marketing executive, personal communication, October 23, 2023).
In-game purchases have minimal impact on player retention. Only 28% of respondents claimed to purchase DLC, accessories, skins, and other customizations monthly. Similarly, almost half (47%) of our respondents have either never made in-game purchases, or only make a purchase once a year. The most common motivators for in-game purchases are because they look cool, players identify with the character, and/or they are coupled with special in-game abilities. We also asked if our respondents have ever purchased a battle pass, in which 43% reported they have never done so. Our survey findings revealed that although a small percentage of players make purchases within a game, a significant portion of players showed minimal expenditure, which may be a result of consumer frustration and monetization fatigue.
Engagement, Disengagement, and Re-Engagement Factors
The top engagement factor is “interacting with new content,” as 182 players ranked this as the primary reason they keep playing a game. This is followed by “striving to complete new challenges” and “participating in events/challenges.” The survey also gauged engagement and content preferences by asking respondents to recall successful game campaigns. Two of the most recurring answers were the Travis Scott Fortnite concert from 2020 and the “OG Fortnite” campaign, which refers to a seasonal update of the game in November 2023 where Fortnite reintroduced the “OG” (original) 2017 version of the game’s maps and weapons. These campaign recognitions drew out common themes of player demand for cross-media integrations and reliving feelings of nostalgia.
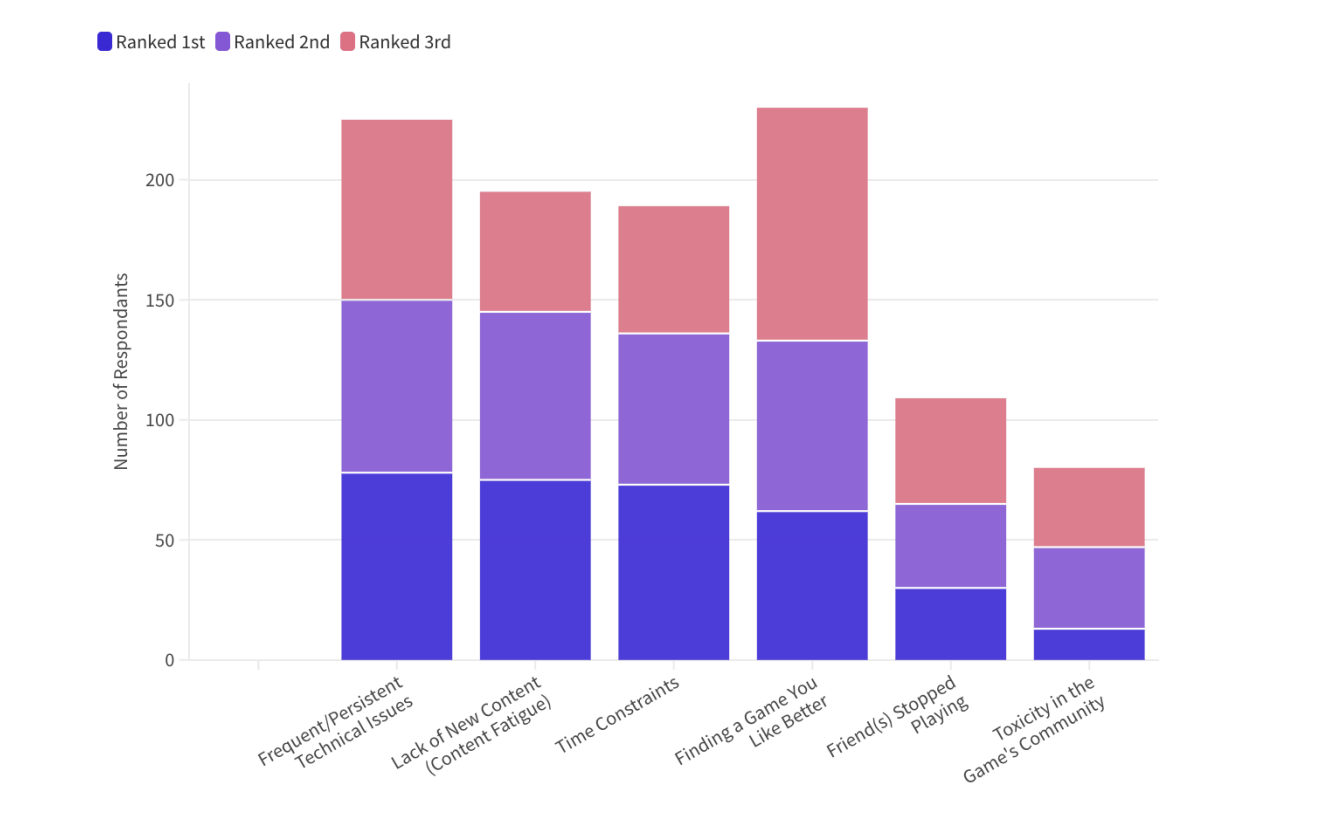
The top four disengagement factors for players, as shown in Figure 2, are nearly equally split between time constraints, content fatigue, frequent and persistent technical issues, and finding a substitute game. These findings were consistent with those from our interviews, and our secondary research alike.
Figure 2. Factors Influencing Disengagement
Note: Results pulled from survey question: “Please rank the following factors that could influence you to stop playing a specific game.”
Top re-engagement factors include new content releases and increased free time. Some write-in responses about re-engagement included that “the game will go through content droughts and then new content will come out that brings me back into play,” and “because I've been busy and finally have free time.” Overall, understanding player motivation and preferences is integral to managing successful gaming experiences. Our survey provides insights into the social dynamics within gaming communities, player’s consumption behaviors, and factors that influence user engagement and disengagement.
Analysis
The key for player retention and engagement lies in de-emphasizing microtransactions, mining nostalgia in players, delivering consistent and attractive content, and fostering User-Generated Content (UGC). New content containing cross-media collaborations can play a crucial role in both attracting audiences’ impressions and increasing audience engagement. Examples such as the TV show partnership between HBO and The Last of Us and virtual concerts such as Blackpink in PUBG Mobile have proven to be mutually beneficial to both games and the intellectual property they partner with. These collaborations can significantly boost interest among players and increase engagement.
The survey highlighted the importance for game companies to continually enhance game content by addressing technical issues and introducing new features. Technical issues can severely affect player experience, increasing the chance of quitting. To further prevent player churn, it is crucial for games to regularly update in-game features, restructure monetization models to de-emphasize microtransactions, and produce new game content to encourage players' interest. However, creating innovative new content is not easy, as “83% of those surveyed say that the gaming industry is under constant pressure to innovate and create new gaming experiences” (EY, para.3, n.d.). According to our research, one method to increase engagement is catering to nostalgia. Players are more likely to continue playing a game set in a familiar story or environment, particularly when these elements evoke memories of past enjoyable experiences related to the game.
LSGs maintain rampant popularity amongst younger millennials and Gen Z audiences, which contributes to both the age breakdown of our survey participants, and for the motivating factors for making in-game purchases. Players purchasing DLC mainly because the items look cool or allow them to express personality, highlights the importance of offering unique items that distinguish paying gamers from non-paying ones, incentivizing the gamers to purchase in-game accessories. This also emphasizes the need to restructure microtransactions to better service player demands. Our primary and secondary research allowed us to pinpoint necessary industry changes in the direction of restructuring game monetization, catering to player nostalgia, encouraging UGC, and continuing to produce cross-media content in-game.
Key Factors in Game Success
The overall sentiment from both primary and secondary research points to two key factors which can determine the success of a game. To survive in the increasingly competitive gaming market, developers must not only ensure their games are high-quality and playable, but also must continuously collect feedback from their customers through various channels to make timely improvements. Integrating player feedback is essential to ensuring that game offerings align with what the target audience seeks to experience. Meeting consumer demands by embracing UGC and engaging in social listening can result in increased profitability.
Factor One: User Generated Content
Many of the study’s interview subjects agree that allowing for UGC in-game is a pinnacle KPI for developers to adapt. According to Newzoo's Game Performance Monitor, Fortnite was the most-played PC game in February 2024. Fortnite’s launch in September 2017 overshadowed competitors through a lack of technical issues, ease of controls and mechanisms, and a high level of player accessibility, redefining the standard for LSGs (Swan, 2022). Games such as Halo Forge, Minecraft, and Roblox have also experienced monumental success by creating platforms to encourage, manage, and showcase user creations. These games allow their players to create their own value by modifying maps and cosmetics to optimize playing experiences (Carson, 2024). In Halo Forge’s case, “2.3 million unique maps have been created in Halo Forge since its launch [and] 3.2 million hours have been spent playing custom games on Halo Forge maps since the mode launched” (Wakeford, 2023, para. 20-21). Encouraging UGC allows for increased customization, putting the power to design unique experiences in the hands of players.
UGC can simultaneously occur on social platforms outside of the game, giving players a space to share moments of achievement, frustration, and struggles across platforms such as Twitch, Discord, Reddit, and other public forums. Users generating and publishing their own digital and written content outside of the game itself keeps the game circulating among the gaming community at large, and allows players to interact with like-minded gamers. Developers can then use this feedback for social listening to represent the opinions of their respective game populations. These online forums and social groups can “bring people together, break down boundaries, provide feedback and develop social skills” (BG Games, 2023, para. 11). Encouraging players to use social platforms to create communities celebrating a shared interest in a given game, and/or providing in-game playing modes to cater to UGC, can increase engagement and reduce churn.
Factor Two: Importance of Implementing Player Feedback
To remain competitive in the industry, it is imperative for developers to know a player's last action before quitting a game. As a general best practice, developers should “have some arbitrary description of what [players] are doing [prior to leaving a game for an extended time]” (technologist, game designer, and producer, personal communications, December 12, 2023). This information can allow developers to address pain points quickly and effectively to reduce churn. Crossfire, a first-person shooter LSG published by Tencent, analyzed their player experience and used the feedback to improve gameplay to decrease player falloff. Specifically, Crossfire maps were modified to remove the frustration of losing to opponents that take advantage of blind spots, or areas outside of a player’s immediate vision. This action doubled their peak concurrent users (PCUs) by two million, proving the necessity for servicing games according to player feedback (technologist, designer, and producer, personal communication, December 12, 2023).
Developers accounting for UGC on social platforms (such as Reddit or Discord) and creating actionable solutions to pitfalls can optimize player experiences. Minecraft’s developers used social listening to “harness feedback from various sources to shape its concept and vision. It wasn't limited to public feedback alone; it also actively sought input from [the developer’s] peers, other game developers, and industry professionals” (Campbell, n.d., para. 9). The initial success of Minecraft was due to the game concept and vision, created by the demands and desires of the players themselves. Social listening encourages developers to use the resources readily available to them, as “it’s less about innovative tools and more about how innovative you are with using tools that already exist” (product marketer, personal communication, February 5, 2024). Listening to consumers is a free tool that any level of developer can use to keep in touch with their communities and optimize games for their players.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that LSGs must strategically innovate to sustain growth. An overwhelming majority of our survey respondents stated that interacting with new content is the primary reason to continue playing a game and inversely, time constraints and content fatigue are among the top three reasons to stop. Central to creating successful live service game campaigns is relying on the industry’s capacity to evolve and diversify gameplay.
A successful strategy includes restructuring microtransactions to focus more on intrinsic benefits rather than competitive advantages in order to alleviate monetization fatigue and sustain player interest. In addition, fostering nostalgia or incorporating nostalgic elements in-game has demonstrated success in player engagement and retention as seen in examples such as OG Fortnite, Pokemon GO, and Tekken 8. These games showcase the effectiveness of reformatting classic games and/or re-establishing original game sentiments that got players intrigued in the first place. Another strategy is to introduce tiering systems for diverse game modes which can accommodate players of varying skill levels. In line with tiered game modes is the power of UGC, giving players the power to shape their gaming experience. Lastly, leveraging successful integrations of media beyond the gaming space enables developers to enhance in-game experiences by tapping into the visibility and popularity of external partnerships, thereby sustaining and revitalizing engagement.
The future of LSGs is fueled by the boundless creativity of both developers and players. As the industry evolves, there will be an inevitable shift towards a more player-centric approach, where developers actively engage and respond to player feedback. This symbiotic relationship not only fosters a deeper sense of community but also paves the way for an array of new experiences, promising a new era of immersive entertainment.
-
ActivePlayer.io. (2024, March 22). Dragon’s dogma 2 live player count & statistics (2024). The Game Statistics Authority : ActivePlayer.io. https://activeplayer.io/dragons-dogma-2/
Aura (Outfit). (n.d.) Fortnite Wiki. https://fortnite.fandom.com/wiki/Aura_(Outfit)
Bankhurst, A. (2023, November 5). Fortnite Just Had Its “Biggest Day” Ever Thanks to Fortnite OG With Over 44.7 Million Players. https://www.ign.com/articles/fortnite-just-had-its-biggest-day-ever-thanks-to-fortnite-og with-over-447-million-players
BG Games. (2023, August 16). Gaming communities: The rise and impact of gaming communities on the world of video games. Medium. https://bggames.medium.com/gaming-communities-the-rise-and-impact-of-gaming-communities-on-the-world-of-video-games-1fec152f649f
Black, S. (2024, January 10). Apex Legends players fed up with game’s “Poor” state as it bleeds users. Dexerto. https://www.dexerto.com/apex-legends/apex-legends-players-fed-up-with-games-poor-state-as-it-bleeds-users-2469889/
Borman, M. (2023, July 17). Gaming’s live-service focus will have to face the reaper sooner or later. Game Rant. https://gamerant.com/live-service-games-how-many-cannibalize-time-money-gameplay/
Breslin, R. L. (2024, January 11). Gamers are begging publishers to put single-player stories over live-service. GAMINGbible. https://www.gamingbible.com/news/gamers-begging-publishers-single-player-over-live-service-948999-20240111
Brosofsky, B. (2024, March 2). Helldivers 2 proves live-service games aren’t the real problem. ScreenRant. https://screenrant.com/helldivers-2-life-service-game-pvp-microtransactions-cost/
Campbell, K. (n.d.). The power of player feedback: Why listening to your community is key… Testify. https://www.gotestify.com/resources/the-power-of-player-feedback-why-listening-to-your-community-is-key-to-game-development-success
Carson, O. (2024, March 12). Understanding user-generated content in gaming. PubNub. https://www.pubnub.com/blog/understanding-user-generated-content-in-gaming/
Chaundy, D., Ebanez, K., & Stojković, A. (2024, March 1). Most played games in 2024, ranked by average monthly players. Twinfinite. https://twinfinite.net/features/most-played-games/
Chung, S. (2023, March 30). Live service games are exhausting. IGN. https://www.ign.com/articles/live-service-games-are-exhausting
Clement, J. (2024, March 6). Steam annual game releases 2024. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/552623/number-games-released-steam/
Comparably. (2022). Riot games competitors | comparably. https://www.comparably.com/brands/riotgames?__cf_chl_tk=AGy8_9qRJkNATMXcZYozqX5xN.vRECFbrw_Ly1EsAZQ-1714439850-0.0.1.1-1621
Diaz, A. (2023, November 8). Fortnite OG is super weird as a Zero Build player. https://www.polygon.com/23952544/fortnite-og-map-zero-build-impressions
Dong, A. (2023, October 3). How riot games is cementing its spot in esports and beyond. https://www.fastcompany.com/90957925/riot-games-esports-arcane
Eloking. (n.d.). Season: What is a season in Valorant and League of Legends? https://eloking.com/glossary/general/season
EY. (n.d.). Competition that helps gaming companies innovate. https://www.ey.com/en_us/insights/media-entertainment/what-s-possible-for-the-gaming industry-in-the-next-dimension/chapter-1-competition-that-helps-gaming-companies-innovate
Focus. (n.d.) Fortnite Wiki. https://fortnite.fandom.com/wiki/Focus
Fragen, J. (2024, February 7). U.S. video game spending stagnated in 2023, totaling $57.2B. VentureBeat. https://venturebeat.com/games/esa-circana-us-video-game-spend-57-2b-2023/
Francis, B. (2023, December 27). What the heck is happening with live service games?. Game Developer. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/business/what-the-heck-is-happening-with-live-service games
G2A.com. (2023, March 13). What is a battle pass and how does it work: A newcomer’s guide. G2A News. https://www.g2a.com/news/features/whats-a-battle-pass/
Game Development Report (2023). Retrieved March 3, 2024, from
https://griffingp.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/2023-Game-Development-Report.pdf
Garrity, T. (2022, November 9). Can Ted Lasso save EA Sports?. InsideHook. https://www.insidehook.com/culture/ted-lasso-ea-sports
Gresham, P. (2023, May 19). Live services: Is the success of the few clouding the strategic judgment of the many?. MIDiA Research.
https://www.midiaresearch.com/blog/live-services-is-the-success-of-the-few-clouding-the-strategic-judgement-of-the-many
Hardy, Q. (2016, July 13). Pokémon Go, Millennials’ First Nostalgia Blast. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2016/07/14/technology/pokemon-go-millennials-first-nostalgia-blast.html
Hurych, A. (2024, April 19). All upcoming video game release dates in 2024. TheGamer. https://www.thegamer.com/video-game-release-dates-2024/
I changed my name to “Beat me to win all my credits” in Rocket League & this insane trade happened! (2022, August 9). YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=03UVjIsEVt8
Kaser, R. (2024, January 23). Subscriptions, live service games will slow down in 2024 | newzoo ... Subscriptions, live service games will slow down in 2024 | Newzoo. https://venturebeat.com/games/subscriptions-live-service-games-will-slow-down-in-2024-newzoo/
Kayes, E. (2016, April 23). You won’t believe how much money GTA Online has made in microtransactions alone. FragHero. https://fraghero.com/you-wont-believe-how-much-money-gta-online-has-made-in-microtransactions-alone/
Kennedy, J. (2023, December 17). 14 most tryhard skins in fortnite. TheGamer. https://www.thegamer.com/sweatiest-fortnite-skins/
Makuch, E. (2017, November 14). Microtransactions, explained: Here’s what you need to know. GameSpot. https://www.gamespot.com/articles/microtransactions-explained-heres-what-you-need-to/1100-6456995/
Mejia, O. (2024, January 30). Live service game sales were 73% of electronic arts (EA) Q3 2024 revenue. Shacknews. https://www.shacknews.com/article/138525/ea-q3-2024-earnings-live-service
Mercante, A. (2022, March 9). Live service game fatigue is real, but can it be fixed?. gamesradar. https://www.gamesradar.com/live-service-game-fatigue-is-real-but-can-it-be-fixed/
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Microtransaction definition & meaning. Merriam-Webster. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/microtransaction
Mills, M. (2024, March 1). Gaming industry layoffs: Key catalysts. Yahoo! Finance. https://finance.yahoo.com/video/gaming-industry-layoffs-key-catalysts-220125538.html?
Most Used Fortnite Skins. Fortnite.GG. (n.d.). https://fortnite.gg/most-used-skins
Naji, S. (2024, February 5). The quick death of new live service games. LinkedIn. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/quick-death-new-live-service-games-sam-naji-horde/
Neese, C. (n.d.). Colan Neese | LinkedIn [Review of Colan Neese | LinkedIn]. LinkedIn. Retrieved March 3, 2024, fromhttps://www.linkedin.com/in/colanneese/
Newzoo. (2023). Top public video game companies | by revenue | newzoo. https://newzoo.com/resources/rankings/top-25-companies-game-revenues
O’Connor, J. (2024, March 3). James O’Connor | LinkedIn [Review of James O’Connor | LinkedIn]. LinkedIn. Retrieved March 3, 2024. from
https://www.linkedin.com/in/jamesxiii/
Ogunnaike, A. (2024, March 4). How Many People Play Pokemon Go: A Look at the Player Count. Esports.net.
https://www.esports.net/news/pokemon/how-many-people-play-pokemon-go
Rathalos11. (2023, April 26). Some new information about Scattered Brains, Inc. https://www.reddit.com/r/oddworld/comments/12z9wrm/some_new_information_about_scattered_brains_inc/
Reeves, B. (2023, December 28). Apex Legends player count dropped by almost 50% on steam this year. Dexerto.https://www.dexerto.com/apex-legends/apex-legends-player-count-drop-steam-2023-2448933/
Removing player-to-player trading in December. (2023, October 10). Rocket League ® - Official Site. https://www.rocketleague.com/en/news/removing-playertoplayer-trading-in-december
Selway, J. (2023, November 14). The success of Fortnite og leaves the game in a tough spot. Game Rant. https://gamerant.com/fortnite-og-success-future-status/
Snegiev, S. (2023, November 9). The dying art of boredom in game design: The toll of monetization on creativity. HackerNoon. https://hackernoon.com/the-dying-art-of-boredom-in-game-design-the-toll-of-monetization-on-creativity
Sorek, S. (2024, January 12). To mod or not to mod: Why the future of gaming is user generated. Game Developer. https://www.gamedeveloper.com/programming/to-mod-or-not-to-mod-why-the-future-of gaming-is-user-generated
Surf Witch. (n.d.) Fortnite Wiki. https://fortnite.fandom.com/wiki/Surf_Witch
Swan, C. (2022, September 26). Fortnite 5 Years Later - Becoming a Worldwide Phenomenon. Game Rant. https://gamerant.com/fortnite-5-year-anniversary-worldwide-phenomenon-epic-games-massive-success/
Tassi, P. (2023, November 10). Sony is cutting its PlayStation Live service calendar in half. Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/paultassi/2023/11/09/sony-is-cutting-its-playstation-live-service-calendar-in-half/?sh=1666fb132622
Taylor, D. (2023, November 23). Fortnite Creative’s Long Road Ahead. https://naavik.co/digest/fortnite-creative-read-ahead/
Taylor, M. (2024, January 23). Tekken 8 Review. PC Gamer. https://www.pcgamer.com/tekken-8-review/
Tekken 8 Live Player Count & Statistics (2024). The Game Statistics Authority : ActivePlayer.io. (2024, January 30). https://activeplayer.io/tekken-8/
“This is why rocket league content is dying.” | my thoughts as a large Rocket League Content creator. (2023, December 21). YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RmyciH4J8wg
Thompson, C. (2023, April 27). Capitalism is ruining video games. Mother Jones. https://www.motherjones.com/media/2023/04/asphalt-video-games-microtransactions-loot-boxes-in-game-purchases-capitalism/
Valentine, R. (2020, December 1). Travis Scott reportedly grossed roughly $20m for Fortnite Concert appearance. GamesIndustry.biz. https://www.gamesindustry.biz/travis-scott-reportedly-grossed-roughly-usd20m-for-fortnite-concert-appearance/
Video game market (by type: Online, offline; by Platform: Computer, console, Mobile; by business model: Free-to-play, pay-to-play, play-to-earn) - global industry analysis, size, share, growth, trends, regional outlook, and forecast 2024-2033. Precedence Research. (n.d.). https://www.precedenceresearch.com/video-game-market
Wakeford, A. (n.d.). Wintertime wonders. Halo. https://www.halowaypoint.com/news/wintertime-wonders
Wakelin, J. (2024, January 16). Top 5 developments driving growth for video games. PwC. https://www.pwc.com/us/en/tech-effect/emerging-tech/emerging-technology-trends-in-the-gaming-industry.html
Winslow, L. (2022, June 27). Diablo immortal could run your Wallet way more than you thought. Kotaku. https://kotaku.com/diablo-immortal-build-microtransaction-legendary-gem-bl-1849112884
Wirtz, B. (2023, September 7). The best and worst pay to win games. Video Game Design and Development. https://www.gamedesigning.org/gaming/pay-to-win-games/
Ziwei, P. (2020, December 2). Travis Scott reportedly earned $20million from “fortnite” event. NME. https://www.nme.com/news/music/travis-scott-earned-20million-fortnite-concert-event-2829792
Zwiezen, Z. (2024, February 2). Over 500 studios are working on live-service games. Kotaku. https://kotaku.com/live-service-games-95-studios-destiny-suicide-squad-1851221959