As technology reshapes employment, artists face particular financial challenges, earning 30% less than their peers while lacking traditional benefits. This article examines how cities and organizations are testing new solutions—from guaranteed income programs to innovative pension schemes—to provide artists with greater economic stability.
Art Restoration Technologies: Renewing Artwork in the 21st Century
In the visual arts, there is no guarantee that work will be preserved for any time after it has been created. While physical pieces are certainly more permanent that performances, all works are subject to deterioration and destruction. Some pieces are more susceptible, such as work made of fragile material or located in an unstable environment, but all pieces will eventually face wear and damage. Restoration is thus required in order to renew pieces to their original and/or best form. Ultimately, the goal of restoration is to safely and accurately bring pieces to their best form for study and public enjoyment. Through technology, this goal can be accomplished.
Crypto: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly
In recent years, the advancement of cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based technologies has led to increased exploitation from criminals. From “pump and dump” scams to cybercrimes, the rapid rise of digital assets has raised questions about their exploitation by criminals to launder money and commit fraud in untraceable and anonymous ways. Lawmakers and regulators have been trying to figure out ways to combat the threats that the growing sector imposes. On February 17, 2022, the Department of Justice announced its new National Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team (NCET) appointing Eun Young Choi as director. Many argue that the NCET and the FBI’s Virtual Asset Exploitation Unit that launched on February 18, 2022 signals more crackdowns on the crypto industry. As the possibility of regulations looms, what are some of the effects it may bring to the crypto and NFT markets? This article explores what some may look like.
Technology Connecting ICH Motivations and Safeguarding Responsibilities
In an increasingly virtual work environment, digital technology is becoming a standard tool for creative industries. Cultural heritage work is no different. A broad variety of tools are being used to safeguard cultural heritage sites and objects, from partnering 3D modeling, drones and artificial intelligence for a preservation project on the Great Wall of China, to virtual reality being used to replicate and recreate the Dunhuang Caves. With the growing attention for intangible cultural heritage (ICH), it is important to explore what digital tools are being used for fulfilling intangible cultural heritage safeguarding responsibilities and what opportunities exist for other projects and their practitioners.
Intangible Cultural Heritage: Context and Digital Approaches for Safeguarding Efforts
Digitization efforts for cultural heritage are standard practice for institutions of all sizes, ranging from simple metadata records to elaborate 3D renderings of ancient sites. While the discussion of digitally preserving cultural heritage at large is prominent, the intersection of intangible cultural heritage and digitization practices requires specific recognition. This includes understanding intangible cultural heritage and its value for society. This article examines the emerging and evolving landscape of intangible cultural heritage, its global impact, and current efforts for safeguarding these intangible items in order to address how this field is being organized and used.
Cybersecurity Solutions for Remote Work in the New Year
Cybersecurity has been on more people’s radars because of the recently exposed SolarWinds cyberattack, which impacted customers including the United States government. In this particular case, the breach was able to go undetected for months, indicating that even institutions with the highest levels of security can fall victim. As we begin the new year, arts organizations face a timely opportunity to consider their cybersecurity measures for remote work.
Boosting Cybersecurity for Remote Work in the Arts
Remote work generally poses greater security threats to organizations than in-person work since, for example, employees use home networks and access organizational information on personal devices. Even before the Covid-19 pandemic, cybersecurity was becoming a bigger threat for smaller organizations and nonprofits. It may seem fatalistic to ask arts organizations to prepare for the worst cyberattack situation—one that might seem unlikely—but managers should think of cybersecurity as another aspect of making their organization stronger, just like ensuring patrons’ physical safety and protecting the organization’s financial health. Now that the pandemic has forced many aspects of arts organizations’ operations online, managers can use this opportunity to survey their organization’s digital landscape and potentially open the door for more remote work opportunities in normal times.
Social Distancing Strategies in the Arts: Film and TV, Part 3 of 3
As the entertainment and arts industries begin reopening, they face new challenges in light of COVID-19. Each industry is developing unique solutions to keep their audiences and staff safe. Part 3 of this series highlights the emerging trends and new protocols being implemented in the film and tv industries.
Social Distancing Strategies in the Arts: Performing Arts, Part 2 of 3
As arts institutions are in the midst of reopening plans, they are faced with new challenges as they seek to ensure the safety of their visitors, audiences, and staff in the COVID-19 era. The challenges and solutions differ depending on the industry, and whether it is a museum, performing arts institution, or film and television. Part 2 of this 3 part series explores the immerging reopening plans for the performing arts sector.
Social Distancing Strategies in the Arts: Museums, Part 1 of 3
With most major countries outside of the United States going through reopening procedures, social distancing strategies are being implemented to help stagnate or reduce the number of COVID infections. This 3 part series will highlight case studies for the Fine Arts, Theatre, Orchestra, Dance, and Movie Industries, showing measures that have been implemented or recommendations in place for each. Part 1 will focus on the museum space.
The Present & Future of Arts Organizations, Technology, and the Pandemic
As arts managers, we try to keep up with technology changes and upgrades. Adopting technology to support a mission and vision is critical, whether it is to serve an audience directly or make a workspace more efficient. Yet, even when the best strategies are put into place, life derails us, and even the strongest organizations are put to the test.
Why More Arts Organizations Need Privacy Policies
As the need for website privacy policies grows, how are arts organizations keeping up? From a sample of 100 nonprofit arts organizations across the United States, this article evaluates how many organizations have accessible privacy policies on their website and why that number should be higher—both to show their dedication to protecting patrons’ personal data privacy and to keep up with changing policy requirements.
What Arts Nonprofits Should Know About Data Privacy and Security
In a survey of 467 nonprofit professionals, EveryAction and Nonprofit Hub found that 90% of nonprofits are collecting data, but that 49% of surveyed nonprofit professionals did not know how it was collected. While data clearly plays a large role in nonprofit arts organizations’ operations, few have concrete policies and procedures that guide its collection and use. In the context of changing policies about data privacy and increased risk of cyberattacks, this is a dangerous place for nonprofit arts organizations to be in. This article will summarize considerations in areas pertinent to these organizations.
A Digital Future for Cultural Heritage
Digital technology is becoming a standard tool for the collection, preservation, and dissemination efforts of arts and cultural heritage worldwide. From 3D configuration of ancient artifacts to applying artificial intelligence to shed new light on how we perceive the lineage of humanities, cultural heritage is headed toward a digital future. This article will examine the ways in which digitization and artificial intelligence – two of the most widely used or relevant forms of technology in cultural heritage – are applied through global cases of innovative initiatives happening in the field in recent years.
A Simple Guide to Data Analytics for Nonprofits, Part II
More than a trend or a buzzword, data analytics are here to stay. Newcomers to arts management may find themselves asking, what does data analytics mean for me, and how and why does my organization need to use it? If you are new to arts management, or the data world in general, this two part series is for you!
This article is Part II of a two part series. Part I is available here.
Trends in the Nonprofit Sector
Donors and other major funders typically seek quantitative evidence of mission-related impact in communities therefore nonprofit organizations are making data analytics a standard part practice in daily operations. However, the transition into data-driven decision making hos occurred quite slowly, with over two-thirds of nonprofits reporting that they are only in the beginning stages of implementing data analytics. Furthermore, the majority of nonprofits report that they are not using external data for mission-related analysis; it seems that there is a lack of knowledge or disconnect about how big data can be captured for future community impact. In general, larger nonprofits are more likely to implement data analytics in tandem with improved strategic planning for the mission and programming. Smaller nonprofit organizations, or even arts organizations that wish to place on emphasis on people rather than numbers, have access to many of the same data analytics tools as larger counterparts—so the present concern is why are some organizations not implementing these accessible strategies which can have an immediate impact?
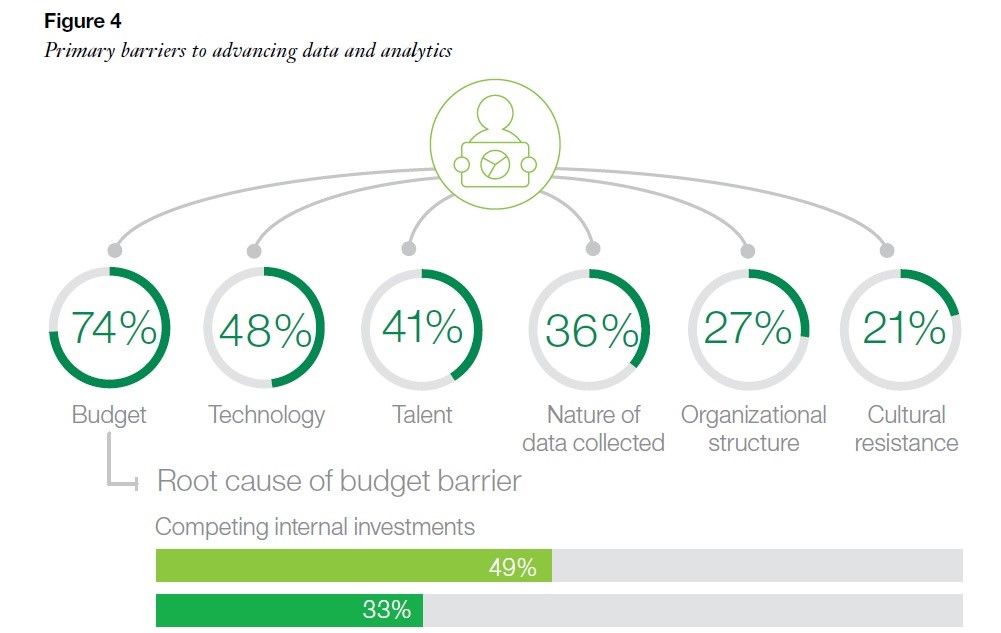
Graph of reasons for not doing data analytic cited by nonprofits: Image credit: IBM, Leap Before You Lag (2017)
Numerous barriers, ranging from internal to external environmental factors, are frequently cited as contributing to an organizations the lack of data analytics use. Particularly for smaller or newly founded organizations, the lack of proper technological infrastructure prohibits even the most basic data analytics collection. Similarly, some organizations cite their limited financial resources. Others are concerned about potential resistance to using data as a primary tool for decision making from major funders and financial decision-makers, such as government supporters and board members. A the perceived lack of expertise within an organization’s staff may also present a barrier.
Some of these challenges may be overcome by training staff in data analytics practices, outsourcing for professional consulting, or creating a staff position specifically for data analysis. Depending on the size and financial status of a nonprofit, each of those options can be a viable solution. Staff can be trained on the more basic analytics tools, and many consulting firms offer services that are specifically tailored to the arts nonprofit sector.
Due to the lack of confidence and informative insight for the implementation of analytics, it is imperative that today’s arts managers initiate a new data-driven operations model in their organizations and make the case to stakeholders. The total digitization of information has created a business environment where institutions cannot maintain long-term success without understanding the importance of data.
Best Practices
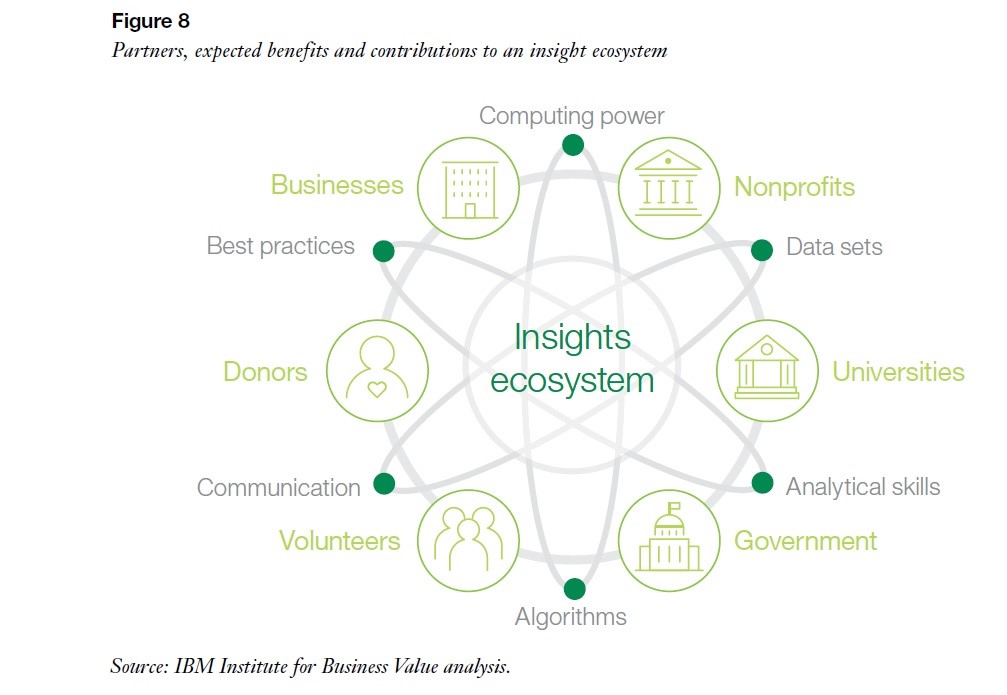
In assessing what type of data to analyze and how to acquire it, arts organizations may benefit from partnering with other nonprofits or seeking assistance from external sources as they begin the journey of analytics-based functioning. As budget constraints are often a prevalent issue, nonprofits may consider a shared data services model and forming an insights ecosystem. This ecosystem is a combination of resources, internal practices, and external information that can help to optimize profitability and mission-focused agendas.
Visualization of an insight ecosystem: Image credit: IBM, Leap Before You Lag (2017)
As demonstrated above, collaboration is actually a key component in the process to becoming a data-driven organization.
A clear strategic plan from a lead staff member concerning the critical nature of data in the arts/nonprofit sector is central to success. There must be a steadfast commitment to using data for major decision-making and a willingness to educate staff and other stakeholders about its benefits. Further, new data practices should align with the financial stipulations set forth by major funders and board members; data analytics must be presented in a way that buttresses the development of mission-based programming for real impact. In terms of internal staff, arts managers need to ensure that “actionable metrics” are defined and the organization invests in the necessary technology to measure said metrics. Data analysis can only be beneficial if the goals are defined and accessible through proper platforms. Consequently, data analytics best practices also require organizational leaders to inform staff of new data-focused operations and empower individuals to improve on their skills in the process. Outsourcing may not be necessary if staff members can be trained on new data software and have the desire to build on their current skillsets. Most important in the data analytics journey is that the emphasis on metrics will build or alter programming in a manner that furthers an arts organization’s mission, vision, and values. The metrics that show evidence of success should be analyzed on an ongoing basis, and should those metrics that show problematic trends should be via immediate changes in budget, programming, staff productivity, or which ever means seems appropriate. Behind all of these best practices lies an individual commitment to seek change; thus, the data analytics truly rests on the “human element” for real-world benefits to be had.
Conclusion
Arts organizations can no longer avoid the use of technology and digitized operational tools in preparing for long-term sustainability. Truly, data analysis is the best method for understanding, evaluating, and changing organizational practices: “Without data, it is impossible to measure financial and operational health, identify problems and measure organizational impact.”The most valuable aspect of data analytics that arts managers should realize is the ability to make relevant organization-wide improvements in alignment with the impact they hope to bring about from their mission statement. While data analysis can effectively aid in the acquisition of donors and retention of key audience segments, nonprofits can use these tools to decide which programming elements are bringing about the community benefits they are seeking (and which are not). Given that an organization’s mission, vision, and values reflect its identity in the community, it would be wise of arts leaders to implement data analytics and become advocates for data-driven decision making.
[1] IBM, “Leap before you lag,” (2017): 1.
[2] Ibid.
[3] Idealware, “The State of Nonprofit Data,” 2.
[4] Ibid., 11.
[5] Ibid., 7.
[6] Ibid., 2.
[7] Ibid., 13.
[8] IBM, “Leap before you lag,” (2017): 14.
[9] Ibid.
[10] Ibid.
[11] Ibid.
[12] Ibid.
[13] Ibid.
[14] Cardinal Path, “The State of Digital Data,” 10.
[15] Idealware, “The State of Nonprofit Data,” 3.
Are You Security Savvy? A Digital Security Quiz
Digital Security & Infrastracture for Arts Organizations - Baseline Considerations
Over the past decade, digital security and infrastructure have arrived at the forefront of the minds of organizations both small and large. In an increasingly digital business world organizations must remain vigilant in protecting the volumes of data they collect. This article examines the baseline considerations for Arts Organizations in relation to managing and protecting both business and patron-side data.
Putting the ARTs in SmART Cities
Advocating For The Arts: Yes You Can
The Giving Pledge: A Start to Engage Tech Philanthropy
To understand why arts organizations have struggled to capture funds from tech billionaires, arts managers and development professionals would do well to recognize what philanthropic sectors they are losing these dollars to, and why. Armed with these insights, arts professionals can then adjust their strategies to better appeal to this new and growing donor segment.